International workshop in poland!
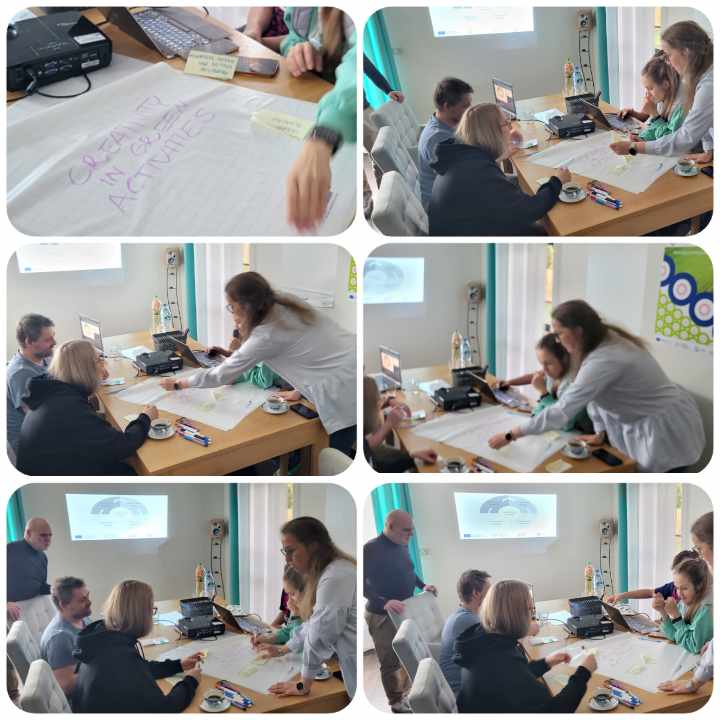
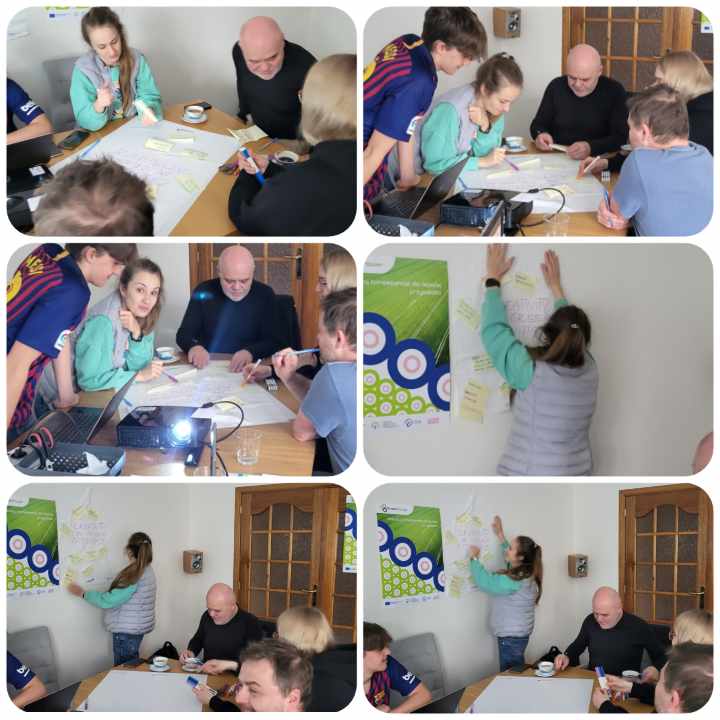
According to the announcements, on April 19-20, 2024, we conducted international workshops as part of the “Green Power” project.
European documents and educational programs often refer to creativity and critical thinking skills as key competencies necessary for personal development, active citizenship, social integration, and employment. Although different documents may define these concepts slightly differently, there is general consensus on their importance and role in education and the development of young people. In 2018, the European Union updated the European Framework for Key Competences, recognizing creativity and critical thinking skills as two of the eight key competences needed by every citizen for personal fulfillment, development, social integration, and employment. This framework emphasizes that creativity and critical thinking are essential for innovation and the social and economic development of Europe. During the workshops, we deepened these concepts and worked on their development.
Creativity is often defined as the ability to generate or recognize ideas, alternatives, or possibilities that may be useful in problem-solving, communication with others, and entertainment. In the context of European educational programs, creativity is understood as a key competence that enables young people to think in innovative ways, find innovative solutions, and adapt to changing circumstances.
Critical thinking skills refer to the ability to think logically, analyze, and evaluate arguments and evidence. They also include the ability to identify errors in thinking, reasoning, and argumentation.
In European policy documents and educational programs, critical thinking skills are seen as essential for personal development, education, active participation in democratic society, and in the job market.
Programs supporting the development of these competencies include: EIT Climate-KIC Young Innovators – a program of the European Institute of Innovation and Technology (EIT), which focuses on education in innovation and entrepreneurship for young people, with an emphasis on challenges related to climate change and sustainable development. “Coding for Kids” programs – an initiative aimed at teaching programming and computational thinking from an early age. Programming develops not only technical skills but also creativity, problem-solving, and critical thinking. The European Youth Foundation (EYF) finances youth projects that promote democracy, human rights, intercultural cooperation, and the development of young people’s skills, including creativity and critical thinking. Various programs were presented during the workshops, aimed not only at developing specific skills but also at promoting openness, tolerance, and intercultural understanding among young Europeans.
Partners created a mind map structure covering key areas related to the creativity of young people:
Center: Creativity of the Young Generation
Main Branches:
A. Areas of Creativity Manifestation
Education: Innovative approaches to learning and teaching.
Entrepreneurship: Startups, innovative business models.
Art and culture: Music, visual arts, theater, dance.
Technology and innovation: App development, programming, new technologies.
Community and social activity: Social projects, volunteering, local initiatives.
B. Factors Influencing Creativity Development
Education and training: Programs supporting the development of creative skills.
Access to resources: Materials, space, technologies.
Social support: Family, school, mentors, online communities.
Social and environmental challenges: Responding to current environmental, social, and economic challenges.
C. Benefits of Creativity
Personal development: Increased self-confidence, problem-solving skills.
Social innovations: Creating solutions for social and environmental problems.
Impact on the labor market: Creativity as a key competence in the job market.
Economic development: Impact on the economy through innovative businesses and startups.
D. Challenges and Barriers
Limitations of the education system: Lack of space for creativity in the traditional education system.
Access to resources: Financial and technological barriers.
Social pressure and fear of failure: Concerns about assessment and failure.
E. Strategies for Developing Creativity
Teaching and learning methods: Project-based learning, design thinking.
Creative spaces: Incubators, coworking spaces, workshops.
Support networks: Mentoring groups, online communities, entrepreneur networks.
F. Creativity in Sustainable Development Actions
Application of Creativity in Sustainable Waste Management
Creativity in Environmental Protection
The workshops were very creative, active, and dynamic. All partners were engaged in the work during two intense days!